=====================================================
HEVC源码分析文章列表:
【解码 -libavcodec HEVC 解码器】
=====================================================
本文分析FFmpeg的libavcodec中的HEVC解码器的主干部分。“主干部分”是相对于“CTU解码”、 “环路滤波”这些细节部分而言的。它包括了HEVC解码器直到hls_decode_entry()前面的函数调用关系(hls_decode_entry()后面就是HEVC解码器的细节部分,主要包括了“CTU解码”、 “环路滤波”2个部分)。
函数调用关系图
FFmpeg HEVC解码器主干部分在整个HEVC解码器中的位置例如以下图所看到的。ff_hevc_decoder
ff_hevc_decoder是HEVC解码器相应的AVCodec结构体。该结构体的定义位于libavcodec\hevc.c,例如以下所看到的。AVCodec ff_hevc_decoder = { .name = "hevc", .long_name = NULL_IF_CONFIG_SMALL("HEVC (High Efficiency Video Coding)"), .type = AVMEDIA_TYPE_VIDEO, .id = AV_CODEC_ID_HEVC, .priv_data_size = sizeof(HEVCContext), .priv_class = &hevc_decoder_class, .init = hevc_decode_init, .close = hevc_decode_free, .decode = hevc_decode_frame, .flush = hevc_decode_flush, .update_thread_context = hevc_update_thread_context, .init_thread_copy = hevc_init_thread_copy, .capabilities = CODEC_CAP_DR1 | CODEC_CAP_DELAY | CODEC_CAP_SLICE_THREADS | CODEC_CAP_FRAME_THREADS, .profiles = NULL_IF_CONFIG_SMALL(profiles),};从源码能够看出。HEVC解码器初始化函数是hevc_decode_init()。解码函数是hevc_decode_frame(),关闭函数是hevc_decode_free()。 hevc_decode_init()
hevc_decode_init()用于初始化HEVC解码器。该函数的定义例如以下。
//初始化HEVC解码器static av_cold int hevc_decode_init(AVCodecContext *avctx){ HEVCContext *s = avctx->priv_data; int ret; //初始化CABAC ff_init_cabac_states(); avctx->internal->allocate_progress = 1; //为HEVCContext中的变量分配内存空间 ret = hevc_init_context(avctx); if (ret < 0) return ret; s->enable_parallel_tiles = 0; s->picture_struct = 0; if(avctx->active_thread_type & FF_THREAD_SLICE) s->threads_number = avctx->thread_count; else s->threads_number = 1; //假设AVCodecContext中包括extradata。则解码之 if (avctx->extradata_size > 0 && avctx->extradata) { ret = hevc_decode_extradata(s); if (ret < 0) { hevc_decode_free(avctx); return ret; } } if((avctx->active_thread_type & FF_THREAD_FRAME) && avctx->thread_count > 1) s->threads_type = FF_THREAD_FRAME; else s->threads_type = FF_THREAD_SLICE; return 0;} 从源码中能够看出,hevc_decode_init()对HEVCContext中的变量做了一些初始化工作。当中调用了一个函数hevc_init_context()用于给HEVCContext中的变量分配内存空间。 hevc_init_context()
hevc_init_context()用于给HEVCContext中的变量分配内存空间。该函数的定义例如以下所看到的。//为HEVCContext中的变量分配内存空间static av_cold int hevc_init_context(AVCodecContext *avctx){ HEVCContext *s = avctx->priv_data; int i; s->avctx = avctx; s->HEVClc = av_mallocz(sizeof(HEVCLocalContext)); if (!s->HEVClc) goto fail; s->HEVClcList[0] = s->HEVClc; s->sList[0] = s; s->cabac_state = av_malloc(HEVC_CONTEXTS); if (!s->cabac_state) goto fail; s->tmp_frame = av_frame_alloc(); if (!s->tmp_frame) goto fail; s->output_frame = av_frame_alloc(); if (!s->output_frame) goto fail; for (i = 0; i < FF_ARRAY_ELEMS(s->DPB); i++) { s->DPB[i].frame = av_frame_alloc(); if (!s->DPB[i].frame) goto fail; s->DPB[i].tf.f = s->DPB[i].frame; } s->max_ra = INT_MAX; s->md5_ctx = av_md5_alloc(); if (!s->md5_ctx) goto fail; ff_bswapdsp_init(&s->bdsp); s->context_initialized = 1; s->eos = 0; return 0;fail: hevc_decode_free(avctx); return AVERROR(ENOMEM);} hevc_decode_free()
hevc_decode_free()用于关闭HEVC解码器。该函数的定义例如以下所看到的。//关闭HEVC解码器static av_cold int hevc_decode_free(AVCodecContext *avctx){ HEVCContext *s = avctx->priv_data; int i; pic_arrays_free(s); av_freep(&s->md5_ctx); for(i=0; i < s->nals_allocated; i++) { av_freep(&s->skipped_bytes_pos_nal[i]); } av_freep(&s->skipped_bytes_pos_size_nal); av_freep(&s->skipped_bytes_nal); av_freep(&s->skipped_bytes_pos_nal); av_freep(&s->cabac_state); av_frame_free(&s->tmp_frame); av_frame_free(&s->output_frame); for (i = 0; i < FF_ARRAY_ELEMS(s->DPB); i++) { ff_hevc_unref_frame(s, &s->DPB[i], ~0); av_frame_free(&s->DPB[i].frame); } for (i = 0; i < FF_ARRAY_ELEMS(s->vps_list); i++) av_buffer_unref(&s->vps_list[i]); for (i = 0; i < FF_ARRAY_ELEMS(s->sps_list); i++) av_buffer_unref(&s->sps_list[i]); for (i = 0; i < FF_ARRAY_ELEMS(s->pps_list); i++) av_buffer_unref(&s->pps_list[i]); s->sps = NULL; s->pps = NULL; s->vps = NULL; av_buffer_unref(&s->current_sps); av_freep(&s->sh.entry_point_offset); av_freep(&s->sh.offset); av_freep(&s->sh.size); for (i = 1; i < s->threads_number; i++) { HEVCLocalContext *lc = s->HEVClcList[i]; if (lc) { av_freep(&s->HEVClcList[i]); av_freep(&s->sList[i]); } } if (s->HEVClc == s->HEVClcList[0]) s->HEVClc = NULL; av_freep(&s->HEVClcList[0]); for (i = 0; i < s->nals_allocated; i++) av_freep(&s->nals[i].rbsp_buffer); av_freep(&s->nals); s->nals_allocated = 0; return 0;} 从源码能够看出,hevc_decode_free()释放了HEVCContext中的内存。 hevc_decode_frame()
hevc_decode_frame()是HEVC解码器中最关键的函数。用于解码一帧数据。该函数的定义例如以下所看到的。
/* * 解码一帧数据 * * 凝视:雷霄骅 * leixiaohua1020@126.com * http://blog.csdn.net/leixiaohua1020 * */static int hevc_decode_frame(AVCodecContext *avctx, void *data, int *got_output, AVPacket *avpkt){ int ret; HEVCContext *s = avctx->priv_data; //没有输入码流的时候。输出解码器中剩余数据 //相应“Flush Decoder”功能 if (!avpkt->size) { //第3个參数flush取值为1 ret = ff_hevc_output_frame(s, data, 1); if (ret < 0) return ret; *got_output = ret; return 0; } s->ref = NULL; //解码一帧数据 ret = decode_nal_units(s, avpkt->data, avpkt->size); if (ret < 0) return ret; /* verify the SEI checksum */ if (avctx->err_recognition & AV_EF_CRCCHECK && s->is_decoded && s->is_md5) { ret = verify_md5(s, s->ref->frame); if (ret < 0 && avctx->err_recognition & AV_EF_EXPLODE) { ff_hevc_unref_frame(s, s->ref, ~0); return ret; } } s->is_md5 = 0; if (s->is_decoded) { av_log(avctx, AV_LOG_DEBUG, "Decoded frame with POC %d.\n", s->poc); s->is_decoded = 0; } if (s->output_frame->buf[0]) { //输出解码后数据 av_frame_move_ref(data, s->output_frame); *got_output = 1; } return avpkt->size;} 从源码能够看出。hevc_decode_frame()依据输入的AVPacket的data是否为NULL分成两个情况: (1)AVPacket的data为NULL的时候。代表没有输入码流。这时候直接调用ff_hevc_output_frame()输出解码器中缓存的帧。 (2)AVPacket的data不为NULL的时候。调用decode_nal_units()解码输入的一帧数据的NALU。以下看一下一帧NALU的解码函数decode_nal_units()。
decode_nal_units()
decode_nal_units()用于解码一帧NALU。该函数的定义例如以下所看到的。//解码一帧数据static int decode_nal_units(HEVCContext *s, const uint8_t *buf, int length){ int i, consumed, ret = 0; s->ref = NULL; s->last_eos = s->eos; s->eos = 0; /* split the input packet into NAL units, so we know the upper bound on the * number of slices in the frame */ s->nb_nals = 0; while (length >= 4) { HEVCNAL *nal; int extract_length = 0; if (s->is_nalff) { int i; for (i = 0; i < s->nal_length_size; i++) extract_length = (extract_length << 8) | buf[i]; buf += s->nal_length_size; length -= s->nal_length_size; if (extract_length > length) { av_log(s->avctx, AV_LOG_ERROR, "Invalid NAL unit size.\n"); ret = AVERROR_INVALIDDATA; goto fail; } } else { /* search start code */ //查找起始码0x000001 while (buf[0] != 0 || buf[1] != 0 || buf[2] != 1) { ++buf; --length; if (length < 4) { av_log(s->avctx, AV_LOG_ERROR, "No start code is found.\n"); ret = AVERROR_INVALIDDATA; goto fail; } } //找到后,跳过起始码(3Byte) buf += 3; length -= 3; } if (!s->is_nalff) extract_length = length; if (s->nals_allocated < s->nb_nals + 1) { int new_size = s->nals_allocated + 1; HEVCNAL *tmp = av_realloc_array(s->nals, new_size, sizeof(*tmp)); if (!tmp) { ret = AVERROR(ENOMEM); goto fail; } s->nals = tmp; memset(s->nals + s->nals_allocated, 0, (new_size - s->nals_allocated) * sizeof(*tmp)); av_reallocp_array(&s->skipped_bytes_nal, new_size, sizeof(*s->skipped_bytes_nal)); av_reallocp_array(&s->skipped_bytes_pos_size_nal, new_size, sizeof(*s->skipped_bytes_pos_size_nal)); av_reallocp_array(&s->skipped_bytes_pos_nal, new_size, sizeof(*s->skipped_bytes_pos_nal)); s->skipped_bytes_pos_size_nal[s->nals_allocated] = 1024; // initial buffer size s->skipped_bytes_pos_nal[s->nals_allocated] = av_malloc_array(s->skipped_bytes_pos_size_nal[s->nals_allocated], sizeof(*s->skipped_bytes_pos)); s->nals_allocated = new_size; } s->skipped_bytes_pos_size = s->skipped_bytes_pos_size_nal[s->nb_nals]; s->skipped_bytes_pos = s->skipped_bytes_pos_nal[s->nb_nals]; nal = &s->nals[s->nb_nals]; consumed = ff_hevc_extract_rbsp(s, buf, extract_length, nal); s->skipped_bytes_nal[s->nb_nals] = s->skipped_bytes; s->skipped_bytes_pos_size_nal[s->nb_nals] = s->skipped_bytes_pos_size; s->skipped_bytes_pos_nal[s->nb_nals++] = s->skipped_bytes_pos; if (consumed < 0) { ret = consumed; goto fail; } ret = init_get_bits8(&s->HEVClc->gb, nal->data, nal->size); if (ret < 0) goto fail; hls_nal_unit(s); if (s->nal_unit_type == NAL_EOB_NUT || s->nal_unit_type == NAL_EOS_NUT) s->eos = 1; buf += consumed; length -= consumed; } /* parse the NAL units */ for (i = 0; i < s->nb_nals; i++) { int ret; s->skipped_bytes = s->skipped_bytes_nal[i]; s->skipped_bytes_pos = s->skipped_bytes_pos_nal[i]; //解码NALU ret = decode_nal_unit(s, s->nals[i].data, s->nals[i].size); if (ret < 0) { av_log(s->avctx, AV_LOG_WARNING, "Error parsing NAL unit #%d.\n", i); goto fail; } }fail: if (s->ref && s->threads_type == FF_THREAD_FRAME) ff_thread_report_progress(&s->ref->tf, INT_MAX, 0); return ret;} 从源码能够看出。decode_nal_units()中又调用了还有一个函数decode_nal_unit(),两者的名字仅仅相差一个“s”。 由此能够看出decode_nal_unit()作用是解码一个NALU。
decode_nal_unit()
decode_nal_unit()用于解码一个NALU。该函数的定义例如以下所看到的。//解码一个NALUstatic int decode_nal_unit(HEVCContext *s, const uint8_t *nal, int length){ HEVCLocalContext *lc = s->HEVClc; GetBitContext *gb = &lc->gb; int ctb_addr_ts, ret; ret = init_get_bits8(gb, nal, length); if (ret < 0) return ret; ret = hls_nal_unit(s); if (ret < 0) { av_log(s->avctx, AV_LOG_ERROR, "Invalid NAL unit %d, skipping.\n", s->nal_unit_type); goto fail; } else if (!ret) return 0; switch (s->nal_unit_type) { case NAL_VPS: //解析VPS ret = ff_hevc_decode_nal_vps(s); if (ret < 0) goto fail; break; case NAL_SPS: //解析SPS ret = ff_hevc_decode_nal_sps(s); if (ret < 0) goto fail; break; case NAL_PPS: //解析PPS ret = ff_hevc_decode_nal_pps(s); if (ret < 0) goto fail; break; case NAL_SEI_PREFIX: case NAL_SEI_SUFFIX: //解析SEI ret = ff_hevc_decode_nal_sei(s); if (ret < 0) goto fail; break; case NAL_TRAIL_R: case NAL_TRAIL_N: case NAL_TSA_N: case NAL_TSA_R: case NAL_STSA_N: case NAL_STSA_R: case NAL_BLA_W_LP: case NAL_BLA_W_RADL: case NAL_BLA_N_LP: case NAL_IDR_W_RADL: case NAL_IDR_N_LP: case NAL_CRA_NUT: case NAL_RADL_N: case NAL_RADL_R: case NAL_RASL_N: case NAL_RASL_R: //解析Slice //解析Slice Header ret = hls_slice_header(s); if (ret < 0) return ret; if (s->max_ra == INT_MAX) { if (s->nal_unit_type == NAL_CRA_NUT || IS_BLA(s)) { s->max_ra = s->poc; } else { if (IS_IDR(s)) s->max_ra = INT_MIN; } } if ((s->nal_unit_type == NAL_RASL_R || s->nal_unit_type == NAL_RASL_N) && s->poc <= s->max_ra) { s->is_decoded = 0; break; } else { if (s->nal_unit_type == NAL_RASL_R && s->poc > s->max_ra) s->max_ra = INT_MIN; } if (s->sh.first_slice_in_pic_flag) { ret = hevc_frame_start(s); if (ret < 0) return ret; } else if (!s->ref) { av_log(s->avctx, AV_LOG_ERROR, "First slice in a frame missing.\n"); goto fail; } if (s->nal_unit_type != s->first_nal_type) { av_log(s->avctx, AV_LOG_ERROR, "Non-matching NAL types of the VCL NALUs: %d %d\n", s->first_nal_type, s->nal_unit_type); return AVERROR_INVALIDDATA; } if (!s->sh.dependent_slice_segment_flag && s->sh.slice_type != I_SLICE) { ret = ff_hevc_slice_rpl(s); if (ret < 0) { av_log(s->avctx, AV_LOG_WARNING, "Error constructing the reference lists for the current slice.\n"); goto fail; } } //解码 Slice Data if (s->threads_number > 1 && s->sh.num_entry_point_offsets > 0) ctb_addr_ts = hls_slice_data_wpp(s, nal, length); else ctb_addr_ts = hls_slice_data(s); if (ctb_addr_ts >= (s->sps->ctb_width * s->sps->ctb_height)) { s->is_decoded = 1; } if (ctb_addr_ts < 0) { ret = ctb_addr_ts; goto fail; } break; case NAL_EOS_NUT: case NAL_EOB_NUT: s->seq_decode = (s->seq_decode + 1) & 0xff; s->max_ra = INT_MAX; break; case NAL_AUD: case NAL_FD_NUT: break; default: av_log(s->avctx, AV_LOG_INFO, "Skipping NAL unit %d\n", s->nal_unit_type); } return 0;fail: if (s->avctx->err_recognition & AV_EF_EXPLODE) return ret; return 0;} 从源码能够看出。decode_nal_unit()依据不同的NALU类型调用了不同的处理函数。这些处理函数能够分为两类——解析函数和解码函数,例如以下所看到的。 (1)解析函数(获取信息):当中解析函数在文章《FFmpeg的HEVC解码器源码简单分析:解析器(Parser)部分》已经有过介绍,就不再反复叙述了。解码函数hls_slice_data()完毕了解码Slice的工作,以下看一下该函数的定义。ff_hevc_decode_nal_vps():解析VPS。ff_hevc_decode_nal_sps():解析SPS。ff_hevc_decode_nal_pps():解析PPS。ff_hevc_decode_nal_sei():解析SEI。hls_slice_header():解析Slice Header。(2)解码函数(解码得到图像):hls_slice_data():解码Slice Data。
hls_slice_data()
hls_slice_data()用于解码Slice Data。该函数的定义例如以下所看到的。//解码Slice Datastatic int hls_slice_data(HEVCContext *s){ int arg[2]; int ret[2]; arg[0] = 0; arg[1] = 1; //解码入口函数 s->avctx->execute(s->avctx, hls_decode_entry, arg, ret , 1, sizeof(int)); return ret[0];} 能够看出该函数的源码非常easy,调用了还有一个函数hls_decode_entry()。 hls_decode_entry()
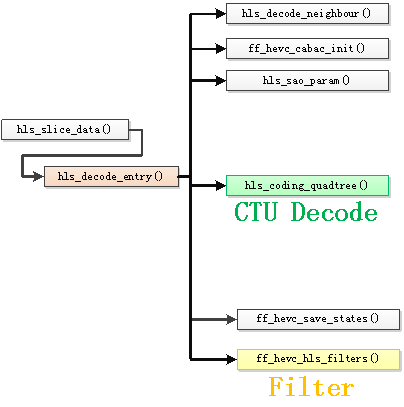
hls_decode_entry()是Slice Data解码的入口函数。该函数的定义例如以下所看到的。/* * 解码入口函数 * * 凝视:雷霄骅 * leixiaohua1020@126.com * http://blog.csdn.net/leixiaohua1020 * */static int hls_decode_entry(AVCodecContext *avctxt, void *isFilterThread){ HEVCContext *s = avctxt->priv_data; //CTB尺寸 int ctb_size = 1 << s->sps->log2_ctb_size; int more_data = 1; int x_ctb = 0; int y_ctb = 0; int ctb_addr_ts = s->pps->ctb_addr_rs_to_ts[s->sh.slice_ctb_addr_rs]; if (!ctb_addr_ts && s->sh.dependent_slice_segment_flag) { av_log(s->avctx, AV_LOG_ERROR, "Impossible initial tile.\n"); return AVERROR_INVALIDDATA; } if (s->sh.dependent_slice_segment_flag) { int prev_rs = s->pps->ctb_addr_ts_to_rs[ctb_addr_ts - 1]; if (s->tab_slice_address[prev_rs] != s->sh.slice_addr) { av_log(s->avctx, AV_LOG_ERROR, "Previous slice segment missing\n"); return AVERROR_INVALIDDATA; } } while (more_data && ctb_addr_ts < s->sps->ctb_size) { int ctb_addr_rs = s->pps->ctb_addr_ts_to_rs[ctb_addr_ts]; //CTB的位置x和y x_ctb = (ctb_addr_rs % ((s->sps->width + ctb_size - 1) >> s->sps->log2_ctb_size)) << s->sps->log2_ctb_size; y_ctb = (ctb_addr_rs / ((s->sps->width + ctb_size - 1) >> s->sps->log2_ctb_size)) << s->sps->log2_ctb_size; //初始化周围的參数 hls_decode_neighbour(s, x_ctb, y_ctb, ctb_addr_ts); //初始化CABAC ff_hevc_cabac_init(s, ctb_addr_ts); //样点自适应补偿參数 hls_sao_param(s, x_ctb >> s->sps->log2_ctb_size, y_ctb >> s->sps->log2_ctb_size); s->deblock[ctb_addr_rs].beta_offset = s->sh.beta_offset; s->deblock[ctb_addr_rs].tc_offset = s->sh.tc_offset; s->filter_slice_edges[ctb_addr_rs] = s->sh.slice_loop_filter_across_slices_enabled_flag; /* * CU示意图 * * 64x64块 * * 深度d=0 * split_flag=1时候划分为4个32x32 * * +--------+--------+--------+--------+--------+--------+--------+--------+ * | | * | | | * | | * + | + * | | * | | | * | | * + | + * | | * | | | * | | * + | + * | | * | | | * | | * + -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- --+ -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- --+ * | | | * | | * | | | * + + * | | | * | | * | | | * + + * | | | * | | * | | | * + + * | | | * | | * | | | * +--------+--------+--------+--------+--------+--------+--------+--------+ * * * 32x32 块 * 深度d=1 * split_flag=1时候划分为4个16x16 * * +--------+--------+--------+--------+ * | | * | | | * | | * + | + * | | * | | | * | | * + -- -- -- -- + -- -- -- -- + * | | * | | | * | | * + | + * | | * | | | * | | * +--------+--------+--------+--------+ * * * 16x16 块 * 深度d=2 * split_flag=1时候划分为4个8x8 * * +--------+--------+ * | | * | | | * | | * + -- --+ -- -- + * | | * | | | * | | * +--------+--------+ * * * 8x8块 * 深度d=3 * split_flag=1时候划分为4个4x4 * * +----+----+ * | | | * + -- + -- + * | | | * +----+----+ * */ /* * 解析四叉树结构。而且解码 * * hls_coding_quadtree(HEVCContext *s, int x0, int y0, int log2_cb_size, int cb_depth)中: * s:HEVCContext上下文结构体 * x_ctb:CB位置的x坐标 * y_ctb:CB位置的y坐标 * log2_cb_size:CB大小取log2之后的值 * cb_depth:深度 * */ more_data = hls_coding_quadtree(s, x_ctb, y_ctb, s->sps->log2_ctb_size, 0); if (more_data < 0) { s->tab_slice_address[ctb_addr_rs] = -1; return more_data; } ctb_addr_ts++; //保存解码信息以供下次使用 ff_hevc_save_states(s, ctb_addr_ts); //去块效应滤波 ff_hevc_hls_filters(s, x_ctb, y_ctb, ctb_size); } if (x_ctb + ctb_size >= s->sps->width && y_ctb + ctb_size >= s->sps->height) ff_hevc_hls_filter(s, x_ctb, y_ctb, ctb_size); return ctb_addr_ts;} 从源码能够看出。hls_decode_entry()以CTB为单位处理输入的视频流。每一个CTB的压缩数据经过以下两个基本步骤进行处理: (1)调用hls_coding_quadtree()对CTB解码。当中包括了CU、PU、TU的解码。 (2)调用ff_hevc_hls_filters()进行滤波。当中包括去块效应滤波和SAO滤波。hls_decode_entry()的函数调用关系例如以下图所看到的。
兴许的几篇文章将会对其调用的函数进行分析。